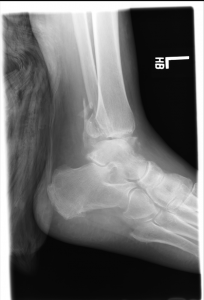
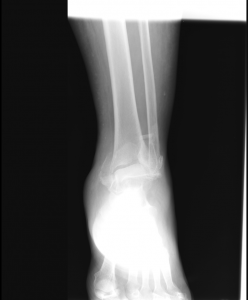
Here’s the xray again.
Patient’s fracture was read as an ankle fracture-dislocation. Posterior dislocation of talus and tibiotalar articulation. Comminuted fractures in distal fibula, posterior malleolus and medial mallelous.
Orthopedics was consulted. Several reduction attempts were made by ortho, but ankle was unstable and reduction was not able to be held by splint. Patient was taken to the OR for reduction and external fixation.
Ankle Fractures:
Types:
- isolated medial malleolus fracture
- isolated lateral malleolus fracture
- bimalleolar and bimalleolar-equivalent fractures (both lateral and medical malleolus involved)
- posterior malleolus fractures
- Bosworth fracture-dislocations (fracture-dislocation of the ankle where the fibula becomes entrapped behind the tibia and becomes irreducible)
- open ankle fractures
Treatment:
Stable: splint or short walking cast
- isolated nondisplaced medial malleolus fracture or tip avulsions
- isolated lateral malleolus fracture with < 3mm displacement and no talar shift
- posterior malleolar fracture with < 25% joint involvement or < 2mm step-off
◦Posterior splint
◦Sugar tong/short leg stirrup splint
Unstable (fracture-dislocation, bimalleolar or trimalleolar fracture, or lateral malleolar fracture with talar shift.)
- ortho consult, possible operative repair (ORIF)
- closed fracture:
o reduction with hematoma block or procedural sedation
- open fracture:
o tetanus
o cover with wet to dry dressing
o ancef
o operative repair
Tintinalli’s Emergency Medicine: A Comprehensive Study Guide
Wheeless’ Textbook of Orthopaedics online
jwang
Latest posts by jwang (see all)
- Xray Vision Answer - May 24, 2015
- Xray Vision: My Arm Looks Funny…. - May 16, 2015
- Xray Vision: Limping Answer - April 27, 2015
- Xray Vision: Limping - April 17, 2015
- Xray Vision: Answer - March 27, 2015