Congratulations Dr. Grundmann!
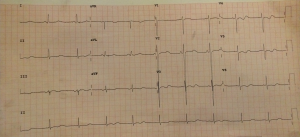
The ECG shows T-wave inversions with prominent U-waves in leads V3-V6, and less prominent in leads II, II, aVF. The QT interval is also prolonged. All signs pointing towards hypokalemia. This patient’s potassium level of 2.3 mEq/L. With the patient’s history of weakness following exertion and his recent consumption of a large carbohydrate meal (two hints), this patient may have a condition called hypokalemic periodic paralysis (HPP).
Hypokalemia definition:
Mild: serum K+ < 3.5
Moderate: serum K+ < 3.0
Severe: serum K+ <2.5
ECG findings associated with hypokalemia:U-waves can have several causes including hypokalemia, hypocalcemia, and hypomagnesemia, although hypokalemia is the most common. No one is sure where U-waves come from but one theory is that they represent delayed repolarization of the His/Purkinje system. These can be independent of the T-wave or on occasion they can merge to produce a double-hump if the T-wave is upright or a biphasic wave if the T-wave is inverted.
A prolonged QTc is also typically seen with hypokalemia. In the case of merged T- and U-waves, the QT interval should be extended to include the U-wave, so the QT interval actually becomes a QU interval. Prolonged QU intervals increase the risk of torsades de pointes or ventricular tachycardia via the ‘R on T’ phenomenon.
ST-depressions may also be seen in hypokalemia, in addition to T-wave flattening/inversion, mimicking subendocardial ischemia. None are present on this ECG.
References:
Lu KC, Hsu YJ, Chiu JS, et al. Effects of potassium supplementation on the recovery of thyrotoxic periodic paralysis. Am J Emerg Med 2004;22:544
Tassone H, Moulin A, Henderson SO. The pitfalls of potassium replacement in thyrotoxic periodic paralysis: a case report and review of the literature. J Emerg Med. 2004;26(2):157.
Life in the Fast Lane: Hypokalemia. http://lifeinthefastlane.com/ecg-library/basics/hypokalaemia/.
Martindale, Jennifer and Brown, David. “Chapter 8. QT Abdnormalities and Electrolyte Disturbanc”. Rapid Interpretation of ECGs in Emergency Medicine. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Willimas & Williams, 2012.
Yonatan
Latest posts by Yonatan (see all)
- Morning Report: 6/29/2015 - June 29, 2015
- Rhythm Nation June 2015 – Answer! - June 20, 2015
- Rhythm Nation June 2015 - June 13, 2015
- Rhythm Nation January 2015 Answer! - January 18, 2015
- Rhythm Nation January 2015 - January 9, 2015