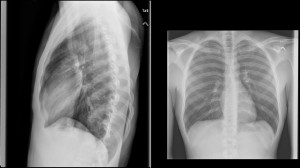
Check out the original post here: Xray Vision: Chest Pain
Congratulations Dr. Grundmann! This patient has a primary spontaneous pneumothorax.
Classification -per American College of Chest Physicians, a small pneumothorax is ≤3 cm from the thoracic apex to lung cupola -per British Thoracic Society, small is considered to be <2cm from thoracic apex to lung cupola Criteria for Stable Patient with Pneumothorax Adapted from Henry M, Arnold T, Harvey J, et al: BTS guidelines for the management of spontaneous pneumothorax. Thorax 58: ii39, 2003; and Currie GP, Allrui R, Christie GL, Legge JS: Pneumothorax: an update. Postgrad Med J 83: 461, 2007. Management -oxygen 3-10L helps increase resorption by 3-4 folds Treatment of Pneumothorax or References: Humphries RL, Young W, Jr.. Chapter 71. Spontaneous and Iatrogenic Pneumothorax. In: Tintinalli JE, Stapczynski J, Ma O, Cline DM, Cydulka RK, Meckler GD, T. eds. Tintinalli’s Emergency Medicine: A Comprehensive Study Guide, 7e. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2011.
Respiratory rate <24 breaths/min
No dyspnea at rest, speaks in full sentences
Pulse >60 and <120 beats/min
Normal blood pressure for patient
Oxygen saturation >90% on room air
Absence of hemothorax
Condition
Treatment Options
Small primary pneumothorax
Observation for 6 h, discharge if no symptoms and return for check if symptoms reoccur or in 24 h
Small-size catheter aspiration with immediate catheter removal, then observe for 6 h, discharge if no symptoms and return for check if symptoms reoccur or in 24 h
or
Small-size catheter or small-size chest tube insertion, Heimlich valve or water-seal drainage, and admission
Small secondary pneumothorax
Small-size catheter or small-size chest tube insertion, Heimlich valve or water-seal drainage, and admission
Large pneumothorax, either primary or secondary, or bilateral pneumothoraces
Moderate-size chest tube and admission; large-size chest tube if fluid or hemothorax present; water-seal drainage and admission
Tension pneumothorax
Immediate needle decompression followed by moderate or large-size chest tube insertion, water-seal drainage, and admission
sliang
Latest posts by sliang (see all)